No one thinks big better than Adam Crowl, a Centauri Dreams regular and mainstay of the Icarus Interstellar attempt to reconfigure the Project Daedalus starship design of the 1970’s. If you’re looking for ideas for science fiction stories, you’ll find them in the essay below, where Adam considers the uses to which we might put the abundant energies of the Sun. Starships are a given, but what about terraforming not just one but many Solar System objects? Can we imagine a distant future when our own Moon is awash with seas, and snow is falling on a Venus in the process of transformation? To keep up with Adam, be sure to check his Crowlspace site regularly. It’s where I found an earlier version of this now updated and revised essay.
By Adam Crowl

By 2025 Elon Musk believes SpaceX can get us to Mars – a journey of about 500 million kilometres, needing a speed of over 100,000 km/h. By comparison travelling to the stars within a human lifetime via the known laws of physics requires energies millions of times more potent than that budget-price trip to Mars. In our energy hungry modern world the prospect seems fanciful, yet we are surrounded by energies and forces of comparable scale. By taming those forces we will be able to launch forth towards the stars, save our civilization and extend the reach of our biosphere.
How so? Consider the sunlight received every second by planet Earth, from the Sun. About 1.4 kilowatts of energy for every square metre directly facing the Sun – all 128 trillion of them – means a total power supply of 175,000 trillion watts (175 petawatts). That’s 8,750 times more than the mere 20 terawatts human beings presently use. Earth itself receives a tiny fraction of the total available – the Sun radiates about 2.2 billion times more, a colossal 385 trillion trillion watts (385 yottawatts).
Just how much does a starship need?
Project Daedalus proposed a fusion propelled star-probe able to fly to nearby stars in 50 years. To do so it would fuse 50,000 tonnes of deuterium and helium-3, expelling them as a rocket exhaust with an effective jet speed of 10,000 km/s. A total useful energy of 2500 million trillion joules (2.5 zettajoules) – the actual fusion energy available in the fuel was about 10 times this, due to the inefficiency of the fusion rocket motor. However that gives us a useful benchmark. Though vast, this is dwarfed by the energy from the Sun. A full Daedalus fuel-tank is equivalent to just 4 hours of sunlight received by planet Earth.

Image: The Daedalus starship, as envisioned by Adrian Mann.
Another design, the Laser-Sail, masses 2,500 metric tons and requires a laser power of 5 petawatts, to accelerate the Laser-Sail starship at 1 gee for 190 days to a cruise speed of half light-speed or 150,000 km/s. A laser-power equal to what Earth intercepts from the Sun, 175 petawatts, could launch ~67 Laser-Sail starships per year. Total energy required per sail is 8.24 yottajoules, equal to 5.45 days of Earth-sunlight.
What else could we do with power supplies that can launch starships? Power on the scale of Worlds (i.e. One Earth = 175 petawatts) allows the remaking of Worlds. Terraforming is the shaping of the dead worlds of the Solar System into more life-friendly environments. Mars, for example, is considered to be the most life-friendly nearby planet other than Earth, yet it lacks an oxygen atmosphere, a significant magnetic field, and is colder than Antarctica. To release Earth-levels of oxygen from its rocks, power an artificial magnetosphere to deflect away the potentially harmful solar-wind, add nitrogen to reduce the fire risk, and keep the planet warm, the energies required are similar to those required to launch starships.
Releasing oxygen from Martian rocks requires melting the rock, usually composed of about 30% oxygen, and breaking the chemical bonds – a process called pyrolysis. What results is a melt of mixed metals, like iron, and semi-metals, like silicon, and oxygen gas, plus some unmelted refractory compounds like aluminum oxide. For every kilogram of oxygen released, about 30 megajoules of energy is needed. Earth-normal oxygen levels require a partial pressure of 20 kilopascals (20 kPa), which means a mass of 5.4 tons of oxygen for every square metre of Martian surface – 775 trillion tons in total. The total energy required is 10 yottajoules.
Adding 80 kPa of nitrogen, like Earth’s atmosphere, requires mining the frozen nitrogen of Neptune’s moon Triton, doubling the total energy required. Pluto’s vast plains of convecting nitrogen ice may provide another possible source, though without the handy proximity of a big planet’s gravity well for getting a boost towards the Sun it might prove uneconomical in energy terms. Shipping it from Saturn’s moon Titan, as Kim Stanley Robinson imagines in his ‘Mars Trilogy’, requires 8 times the energy of using Triton as a source, due to Saturn’s less favourable gravity conditions.
Warming Mars to Earth-like levels, via collecting more solar energy with a vast solar mirror array, means collecting and directing about 50 petawatts of solar energy (equal to about 10 Laser-Sail starships). Before we use that energy to gently warm Mars, it can be concentrated via a “lens” into a solar-torch able to pyrolyse oxygen out of Mars’s rocks. With 50 petawatts of useful energy the lens can liberate sufficient oxygen for breathing in a bit over 6 years.
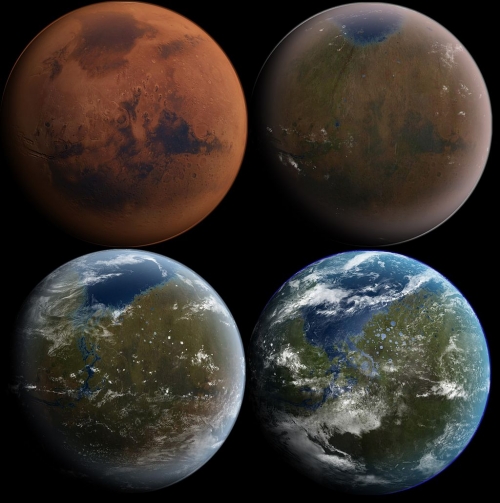

Image: A blue and green Mars emerges from terraforming. Credit: Daein Ballard – The original image was uploaded on en.wikipedia as en:Image:MarsTransitionV.jpg, CC BY-SA 3.0, https://commons.wikimedia.org/w/index.php?curid=939978
The final task, creating an artificial magnetosphere, is puny by comparison. A superconducting magnetic loop, wrapped around the Martian equator, can be used, powered up to a magnetic field energy of ~620,000 trillion joules (620 petajoules), by about 12.4 seconds of energy from the solar-mirrors. This is sufficient to create a magnetosphere about 8 times the size of Mars, much like Earth’s.
Total one-time energy budget is 20 yottajoules – 8,000 “Daedalus” starprobes, or 243 laser-sail starships equivalent. The ongoing power-supply of 50 petawatts is enough to propel 10 Laser-Sail starships at a time.
To terraform the other suitable planets and moons of the Solar System requires similar energy and power levels. For example, if we used a solar-torch to break up the surface ice of Jupiter’s moon, Europa, into hydrogen and oxygen, then used it to ‘encourage’ the excess hydrogen to escape into space, the total energy would be about 8 yottajoules, surprisingly similar to what Mars requires. The nitrogen delivery cost is about 6 yottajoules, again similar to Mars. Ongoing energy supply would be 10 petawatts – two starships worth.
A less exotic location to terraform would be Earth’s Moon. One advantage, as well as proximity to Earth, is no extra input of energy from the Sun is needed to stay warm. However, unlike Europa or Mars, water as well as atmosphere needs to be delivered, multiplying the energy required. If shallow seas are sufficient – an average of 100 metres of water over the whole surface – the energy to deliver ice and nitrogen from Triton, then make oxygen from lunar rocks, is 27 yottajoules.
The only solid planet with close to Earth gravity is Venus. To remake Venus is a vastly more challenging task, as it has three main features that make it un-Earthly: too much atmosphere, too much day-time and not enough water. Take away the atmosphere and the planet would cool rapidly, so while it is often likened to Hell, the comparison is temporary. The energy required to remove 1 kilogram from Venus to infinity is 53.7 megajoules. Venus has over a thousand tons of atmosphere for every square metre of surface – some 467,000 trillion tons of which is carbon dioxide. To remove it all requires 25,600 yottajoules, thus removal is far from being an economical option, even in a future age when yottajoule energy budgets are commonplace.
Another option is to freeze the atmosphere by shading the planet totally. To do so would require placing a vast shade in an orbit between Venus and the Sun, about a million kilometres closer. In this position, the gravity of the Sun and Venus are balanced, allowing the shade to stay fixed in the sky of Venus. With a diameter about twice Venus’s 12,100 kilometres, an endless night produced by the shade would allow Venus to cool down over a period of decades. Eventually the carbon dioxide would rain, then snow, covering the planet in dry-ice. Some form of insulation (foamed rock?) would then be spread over the carbon dioxide to keep it from bursting forth as gas again.
Alternatively it might be pumped into natural cavities, once the sub-surface of Venus is better mapped. The energy cost of assembling such a vast shade, which would mass thousands of tonnes at least, would be far less than the cost of removing the carbon dioxide. So close to the Sun, the shade would intercept the equivalent of 8 times what Earth receives from the Sun – 1,400 petawatts in total, sufficient to propel 280 Laser-Sail starships, or power the terraforming of the other planets. Or both.
The next desirable for Venus is the addition of water. If 100 metres depth is required the total energy to ship it from Triton is 144 yottajoules. Using 50 petawatts of power, the time to export the water is about 122 years, with a 30 year travel time for ice falling Sunwards from Neptune. The total energy of creating an artificial magnetosphere similar in size to Earth’s would be 6 exajoules (6 million trillion joules) – a tiny fraction of the energy budget.
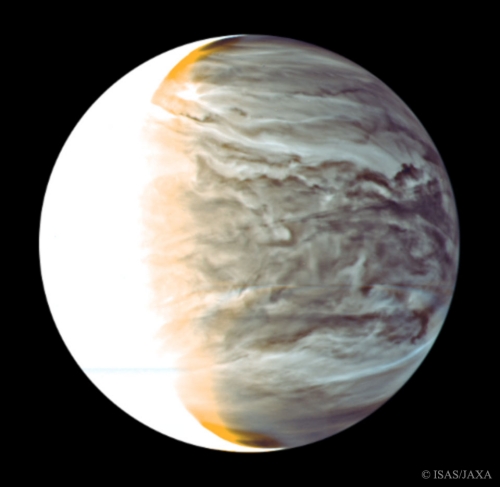
Image: Venus as seen by the Japanese Akatsuki orbiter. The planet was captured in infrared light, showing a surprising amount of atmospheric structure on its night side. The vertical orange terminator stripe between night and day is so wide because of light diffused by Venus’ thick atmosphere. Can we use the Sun’s abundant energies one day to transform this world into a home for life? Credit: ISAS/JAXA.
Further afield than the Inner System and the Outer Planets (including IX, X, XI…) is the Oort Cloud, a spherical swarm of comets thousand to ten thousand times the Earth-Sun distance. According to current planet formation theories there were once thousands of objects, ranging in size from Pluto to Earth’s Moon, which formed out of the primordial disk of gas and dust surrounding the infant Sun. Most coalesced via collisions to form the cores of the big planets, but a significant fraction were slung outwards by gravitational interactions with their bigger siblings, into orbits far from the Sun. One estimate by astronomer Louis Strigari and colleagues hints at 100,000 such objects for every star.
The technology to send a laser beam to a starship accelerating to half light-speed over thousands of Earth-Sun distances opens up that vast new territory we’re only just beginning to discover. A laser able to send 5 petawatts to a Laser-Sail at 1,000 times the Earth-Sun distance, would be able to warm a Pluto-sized planet to Earth-like temperatures at a distance of a light-year. Powering starships will thus enable the spread of the Earth’s biosphere to thousands of worlds which would otherwise remain lifeless. Life on Earth spread out in abundance, aeons ago, once it learnt the trick of harnessing the Sun’s energy via photosynthesis to make food from lifeless chemicals. Bare new volcanic islands are quickly colonised by living things, thanks to the power of the Sun. Humankind can do the same, but on a vastly greater scale – it’s the natural thing to do.



Teraforming Mars and Venus is slow, expensive, dull and unimaginative. Ditto for interstellar vessels with living people. This are the hangover from the caveman era of space exploration – equivalent to refusing to live somewhere unless it has caves.
When we get over this we will realize that planetary surfaces apart from Earth will never be quite right for us, but that’s fine. We can AI-assemble arbitrarily large space stations with temperatures, atmospheres, day lengths and gravity made to specs. It doesn’t even take very much material, or require us to hit some cosmic jackpot of natural habitability. Any solar system with rocks and/or planets is perfectly habitable for humans once we have the right sort of builder AI.
As for getting to these solar systems: we’re not going in generation ships. We will simply send data and fabrication equipment – just enough to boot up the needed assemblers – a civilization seedpod. Living people, animals and plants are among the many things that can be assembled from data and ordinary matter, if you’re clever enough and have some patience. We can even launch the mission before all the data is debugged, since the seed will take centuries to get there and slow to orbit. If it can independently assemble an adequate high-bandwidth antenna, future Terrans will send it much fresher AI to run. For me, this is the only interstellar colonization paradigm that makes any sense.
Well, that’s one opinion. The article as it is conveyed is another.
Regardless of how things happen, ignoring humanity’s instinctive need to explore and experience such exploration first hand will be a motivating force for the exploration. I’ll be so bold to suggest that the ones who have the capital and the will to make this happen will feel entitled (actually will be entitled) to participate and realize some kind of return on investment of time and resources for such exploration. Guess what? While some of these “movers and shakers” may settle for just knowing that in the future, we’ll get EM communications which basically say “we are here, thanks for that,” I think most will seek to enable themselves or their posterity to set foot personally upon the soil (or its equivalent) on a world warmed by another sun.
This latter approach will be more difficult; more challenging than replicating ourselves or some AI at the destination (and the idea of replicating ourselves using then-local resources is akin to invoking magic incantations at this point).
Perhaps this is why you necessitate the need for one or more AI; these may pursue your agenda without “feeling” the need to commit to human desires. Or such AIs may just decide that none of it is worth the effort and demand that we leave the stars alone so that some day truly alien AI may present itself with a better offer.
If we go to the stars, it will happen because someone seeks to overcome the nearly impossible barriers which keep humans from experiencing the journey from inception to arrival, as individuals.
David H,
I said nothing about Generation Ships – the power for fast laser-sails is of the same magnitude as the power to terraform planets. Thus being able to do one means being able to do the other.
If you want to go “Astro-Green” and not indulge in astroengineering then your approach is sensible. There’s plenty of sunlight available for pushing fast-sails to ~0.01c or so. Storing adults as replication patterns – if that can be demonstrated – is a very economical approach in energy terms. However, no scanning system is likely to have perfect fidelity so all such “replicants” will be different people and not the originals. Thus I am sceptical of such being described as “transport” or travel.
Much of the work, especially on Venus, might be done with genetically modified microorganisms.
Do you really think that a living person, or complex life in general, can be fabricated from raw material? This seems like a major jump in technology, even beyond what’s needed to travel at a significant fraction of c. Relativistic travel is a major engineering challenge; but building life, and convincing it to be alive, seems to me like it’s on a higher order of magnitude.
It can be done and requires far less energy than most of the projects presented here.
I’ve been puzzled by this reply all along. Nowhere did I say we should fabricate “a living person” or “complex life in general” from raw material. I was talking about genetic manipulation of bacteria — germs, just germs, microorganisms, I said — that exist here to process the Venusian atmosphere into an earthlike condition. That’s not “building life, and convincing it to be alive”.
We already do such things as engineer sterile insects to mate with their natural counterparts and reduce the next generation to manageable numbers and manipulate immune cells to wipe out diseases in people.
At some point we probably will be able to build organisms from the ground up, but that’s not what I was talking about.
To put things in context, Xcalibur was replying to DavidH. :)
Thanks. It was by my statement so I took it to pertain to mine. That’s why I found it puzzling. I just thought germs could do the job more efficiently and cheaply than vast machines, then either become extinct or adapt.
Yes, that was in reply to DavidH. It was alongside your comment, but not parsed under it in the thread.
I agree that micro-organisms are a valuable tool for terraforming and for other purposes.
As to whether life can be fabricated, I think much depends on abiogenesis, a phenomenon which is not yet properly understood.
I suspect scientists will succeed in fabricating life long before building a spacecraft that can reach a significant percentage of c.
The original rational for building large space colonies was to house builders of large solar power satellites to beam power to earth. That justification no longer makes sense since there are new energy sources being developed.
I agree that people are not going to slow boat to the stars.
We always forget about poor little Mercury, enough energy to generate a staggering magnetic field aided by a large iron core. This magnetic field if aligned parallel to the solar wind would attract a huge amount of solar hydrogen enough for hundreds of thousands of tons of water production per year. And enough energy to convert the surface rock into an oxygen atmosphere in decades or less, just got to prevent recombination by covering it. Enough energy to power interstellar craft by lasers and other duties around the solar system. We could even reduce the surface temperature with a reflective layer to an Earth like one.
‘The final task, creating an artificial magnetosphere, is puny by comparison. A superconducting magnetic loop, wrapped around the Martian equator, can be used, powered up to a magnetic field energy of ~620,000 trillion joules (620 petajoules), by about 12.4 seconds of energy from the solar-mirrors… ‘
They always make the same mistake, use the polar regions where it is nice and cold for superconductors already, two smaller fields one at each pole will link up through the planets iron core (magnetisable) to form a much larger one permanent one.
Hi Michael
Nice. I’m happy with your including Mercury in the picture, though it’s a bit too close to the Sun for terraforming, it’ll definitely play a role in an industrialised Solar System.
As for Mars’s magnetosphere, the twin ring system is probably more practical, but I was simplifying to illustrate the main point, that interstellar energies and terraforming energies are of similar magnitudes.
If you could even contemplate terraforming Mercury than you could conceive of building a shade to regulate the solar insolation to make it effectivly in the habitable zone. Perhaps such a shade could be in the form of millions of orbiting sails designed to self regulate their orbits using the available solar energy. Just daydreaming….
The problem is keeping it stable against instabilities from both light and the solar wind.
Crap–I was hoping we were going to strip-mine Mercury to death, to get the material for the solar power satellites in our Dyson sphere.
Mercury might best be made into a moon for Venus.
Good luck moving it! It’s a lump.
Probably not any more difficult than some of the other ideas here.
It may be better to use the energy of been near the sun and accelerate matter from Mercury passed the Earth to slowly move it saving it for a while from the ever brightening sun.
And Mercury can be paraformed quite well, if we covered the entire surface with a very reflective material and gave it a powerful magnetic field it would hold on to an oxygen atmosphere.
Mercury might be best used as construction material for a future Dyson Swarm, thus allowing Mankind to reach Kardashev Type II.
Although artificial habitats are capable of sustaining many times Earth’s current population, there is a certain romantic attraction to life planetside which, I believe, will not be unpopular. So it’s going to be both choices.
But there are two huge barriers which first need to be traversed. First and foremost, cheap launches (less than $100/Kg) are a prerequisite. Only StarTram and Skylon can deliver here. Secondly, the necessary development of space-based AI/robotics for assembly tasks is likewise almost wholly neglected to date.
I have a problem with that pyrolysis forecast. This link adds to the terraforming discussion, and provides access to a deep bibliography
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=ikoNQNj9ZnU
Let’s see, the Moon’s escape velocity is about 2.8 kps. The average speed of air molecules at room temperature is only about 520 mps. So, we can at least say that the atmosphere wouldn’t leave instantly.
OTOH, that’s uncomfortably close to the Moon’s escape velocity, so atmosphere will be escaping at a significant rate. I believe people have calculated that the Moon could only hold a breathable atmosphere for about 10,000 years.
You could extend that considerably by enclosing the Moon in a large balloon, though. Not joking here, the atmospheric escape is happening at an altitude at which the pressure is vanishingly low; You could support a plastic film, ideally self repairing, at some lower altitude by air pressure, with a vacuum outside it, and considerably extend that time. But you’d need spacecraft to enter and leave through airlocks. Feasible, in as much as space elevators are practical for the Moon even with Kevlar.
So, yes, terraforming the Moon is a technically feasible project, given enough energy and moderately advanced technology. And 25 trillion kilograms of air.
But I’d say it’s actually more useful without an atmosphere, for various purposes as industry.
Slow and expensive projects by contemporary standards, sure. But if those are dull and unimaginative, please sign me up for that tedium.
Step One might be to terraform Terra, so to speak. This article makes me wonder if our imminent climate crisis offers a gateway challenge. The drought and ice crises of the late Pleistocene forced our nearly-extinct savannah ancestors to originate survival technologies that, coincidentally and over time, allowed us to dominate every environment on Earth. Surviving the Anthropocene may require us to develop the first true technology of planetary ecology. There’s probably a Nobel Prize for anyone who learns, for example, how to inexpensively convert large quantities of CO2 into inert sediments straight out of the atmosphere. We’re working on that now with some encouraging results. How might that kind of technology improve the Venus challenge? Help build the hull of a “Rama” habitat out of excess atmosphere while we work on the planet?
Master the complexities of planetary ecology, and not only do we get to go on living on Earth, we eventually get to live anywhere else we want, too.
I suspect Frank Herbert was getting at something like this, with the sandworm as a metaphor for our harshest immediate environment and the Spice, in part, a metaphor for planetary ecology. Mastery of the worm was the mastery of a world, but “he who controls the Spice…”
Anyway, terrific article. Fremen would spit at it. : )
Plants already do a pretty job at that. They are cheap, self-replicating, come in a variety of convenient sizes, and are usually fairly environmentally friendly. I would start there.
In the oceans, coccolithophores and foraminifera are quite efficient at sequestering CO2 as calcium carbonate, as huge strata of limestones demonstrate. The problem is increased acidification of the oceans with increased CO2. What we need is a cheap way to reduce acidity so that these organisms can lay down carbonate rocks more quickly, a preferable approach to algal sequestration as organic matter IMO.
We are in the biological century now. Genetic engineering of organisms is going to be our technological forte. Let’s use these skills and let the organisms get to work. It is nanotechnology that works without magic pixie dust.
If we can bio-engineer cyanobacteria-like bacteria with the ability to “float” in the dense CO2 atmosphere at an altitude of ~50 km and withstand a temperature of about 70°C, they could suck the CO2 out of the atmosphere and transform it in O2, but then as they die they would fall down to the lower layers and burn up in the intense heat, releasing the carbon again that will probably recombine with the O2, unless the carbon is fixed in a molecule that can withstand 740K and 9.3 MPa.
My reply was directed regarding terraforming Earth.
You are quite correct that the Sagan suggestion for removing the CO2 of Venus wouldn’t work. In fact, it wouldn’t work anyway, as organisms need more than just carbon and oxygen to grow and fix carbon.
So we cannot just “seed” the high atmosphere with organisms, we need to create floating bioreactors for this to work, with the bulk of the mass containing water, which is in short supply on Venus.
Shading venus seems like an obvious requirement so that over time the surface will cool. Unfortunately, this could take a very long time.
The alternative approach of building space habitats will allow the solar system to be filled with many orders more of living room in a much shorter period of time.
Coming up with technology that more efficiently mimics (or sure, assists, enhances, synthesizes) native carbon-eaters on the timescales that matter most to us is, unsurprisingly, up to us. Here’s a fresh example of how we look to the Plant Kingdom for inspiration, not just respiration:
http://newsmasterapp.com/article/i6313861216592740868?app_id=1106
And how these technologies might then also be used off-world:
“While the artificial leaf UIC researchers invented is just artificial, not bionic, its applicability isn’t confined to this world. They note it can even be used if water is found on Mars. Mars’s atmosphere is mostly CO2, after all.”
Very good…for future generations not yet born…Meanwhile I keep hoping for a realistic engineering publication about doming over a three mile wide Moon crater, and populating the crater walls with residences for a research station…Much practical experience would be gained at the same time that people learn how best to move further out into the solar system…I guess this is that one baby step logic that Carl Sagan preached…My NASA pub Space Settlements, A Design Study SP-413 (1977) puts me at the doorstep of a realistic space wheel…I’d like a companion pub for doming over a Moon crater for 1,000 people…not ten or twenty…Maybe I want too much, but as Harry S Truman once said, you can always scale back a big dream…
I think I would prefer the “dome” under the crater as described by John Varley in Steel Beach. This provides better radiation and meteor protection and the land surface can be sculpted to have the same curvature as Earth to keep the perspectives and views the same as Earth. The sky would be a projection, or more likely flexible OLED panels to mimic the skies of Earth, changing with a 24 hour cycle, rather than the lunar month. The cost is the drilling.
Small scale starts could be in lava tubes.
What would be useful is a list of these ideas in descending order of energy requirements. Even approximate energy requirements would be a useful resource when discussing approaches. The space of possibilities is huge, but even a sparsely populated list would be of immense value. It would also provide useful targets to improve upon with different approaches. For example, is making Mars a 1/5 bar atmosphere more energy efficient by pyrolysis of rock, or by electrolysis of Ceres water and shipping LOX to mars with solar sails? Or are they about the same?
Good idea, we need to put it under mega engineering projects, maybe under mega – engineering projects via Wiki.
It may be better to leave Venus as it is and mine the planet and clouds in skyships.
‘The energy required to remove 1 kilogram from Venus to infinity is 53.7 megajoules. Venus has over a thousand tons of atmosphere for every square metre of surface – some 467,000 trillion tons of which is carbon dioxide.’
If we could get the deuterium from the outer solar system into crafts that can be propelled at get velocity to Venus we could induce fusion that would rip off the atmosphere in chunks.
‘Another option is to freeze the atmosphere by shading the planet totally. To do so would require placing a vast shade in an orbit between Venus and the Sun, about a million kilometres closer.’
If we could get an asteroid to this Venus-Sun gravity point we could start ripping the asteroid apart and throwing the material outwards to create a sun shade. The material falling to wards the planet and through the atmosphere would react with the sulphuric acid to create a sulphate surface blanket of modest reflectivity opening the lid on the heat below.
‘Eventually the carbon dioxide would rain, then snow, covering the planet in dry-ice. Some form of insulation (foamed rock?) would then be spread over the carbon dioxide to keep it from bursting forth as gas again.’
The planets rock holds a lot of heat which would make it difficult to condense out of the atmosphere.
‘The total energy of creating an artificial magnetosphere similar in size to Earth’s would be 6 exajoules (6 million trillion joules) – a tiny fraction of the energy budget.’
If we had large floating skyships they could be used to create a magnetic field that collected solar hydrogen to create water, the sun loses 1.5 million tons of mass mostly hydrogen per second. If combined with oxygen in the atmosphere that is ~14 millions tons per second, we could not hope to get it all but it still will be a lot.
Why not convert the CO2 to stable carbonates? The trick is getting a cool enough surface to prevent decomposition. The trick might be to build cooled, insulating structures to contain the carbonate. Massive engineering to be sure.
I would think that terraforming Venus is not a great idea. It is already too close to the sun to remain Earthlike without permanent sun shades. Better to construct space cities using the asteroids. More living space, tailored to human requirements, using less energy, and scalable. Planetary terraforming is a huge project that must complete before it is useful.
If we lowered the temperature to around 200-300 C there would be direct combination with the rocky surface to form carbonates. Unfortunately one of the worst GH gases is water vapour, if we put water on the planet it will always be hot even if we take all the CO2 away.
The water needn’t be exposed to the atmosphere. Think reactors sucking in CO2, reacting it with dissolved calcium or magnesium to precipitate out the carbonate.
However this doesn’t even have to be near the ground. Consider huge floating balloons with some water and metal ballast. The CO2 is sucked in, and the precipitate accumulates at the base. Periodically the carbonate is transported to the refrigerated structures on the ground. If low coat access to space is possible, the carbonate could be put into orbit.
As Venus was once a water world, are there deposits of calcium/Magnesium oxides that were once carbonates and had the CO2 baked out of them? These could be used to absorb the CO2 in the high atmosphere balloons.
Atmospheric processors could be used to remove the water from the atmosphere cooling the planet and give floating habitats a lot of water. Once the temperature lowers CO2 will react with the dry soil to form carbonates, we may need to break the ground up to form a porous material to help. We could easily live in the clouds and mine the ground from cables and remote mining vehicles.
We only use about 13% of the Earth in any significant way. The rest is oceans, deserts, and ice caps which are hardly used. Even in the parts that are inhabited, we need buildings to protect us from the natural environment and provide comfortable conditions. If we terraform Mars, we should expect a similar situation. Even if some parts of the planet are brought to reasonable conditions, other parts won’t be.
In particular, the northern half of Mars averages about -5 km relative altitude, while the southern half averages around +3 km, with some parts much higher. So whatever part is the right temperature and pressure, the other part won’t be. Just like Earth, the polar regions will be significantly colder than the Equator. So terraforming will have a poor return on the energy expended, since much of Mars will still require wearing pressure/thermal suits to visit.
To me, it makes more sense to just terraform the areas under your habitat domes. You would need some sort of buildings even if outside pressure and temperature were ideal on average. The significant orbit eccentricity and polar tilt mean strong seasons, and a thicker atmosphere will likely produce weather systems. If you are going to need buildings anyway, you may as well use efficient domes to cover large areas, and dispense with trying to change the rest of the planet.
Underground, just like the moon.
On terraforming Luna, here’s a tongue-in-cheek look. Note the dumb replies, among fewer smart ones–surely a limit on humanity comparable to the admirable energy estimates Adam gives:
http://www.slate.com/articles/technology/future_tense/2014/07/terraforming_the_moon_it_would_be_a_lot_like_florida.html
Intellectually, I always find all the sundry terraforming strategies to be intriguing, as these are.
Aesthetically, however, I always have at least a speed bump of pause as to whether we should remake pristine and unique environments in our own environment’s image. Even if there is not any other-worldly even microbial life involved.
As opposed to instead settling discrete habitats – mostly subterranean but maybe with some smaller above-surface recreational domes so that one can enjoy being (almost) outdoors on the new world without a suit.
The prospect instead of entirely remaking the familiar face of the Moon that we can see most nights – or of what has been the “red planet” Mars since antiquity and beyond – strikes me as somewhat similar to putting terraced condos in the side of the Grand Canyon.
And with full-world terraforming, there’s no carving out of “national park” type refuges preserving the prior natural beauty – stark as that beauty may be in some places but still beautiful – for current and future generations. As best as I can tell, it’s an all-or-nothing proposition with no effective turning back to the status quo ante and no carve outs.
Now, I’m not a tree-hugger by any stretch – and, by definition, we’re talking about there not even being any trees to hug. But, again, I nonetheless have that aesthetic “speed bump of pause” as to whether humankind should terraform rather than merely settle discrete habitats on these other worlds.
If you instead give me some large lump of asteroidal rock or a big iceball in the Kuiper Belt or Oort Cloud, I’m like “science the crap” out of that thing as Mark Watney might say. But pristine and unique environments like the Moon, Venus, and Mars? I’m not so sure.
And if the Sun were expanding into a red giant now rather than aeons from now, that also might present a different issue. But that’s still literally billions of years away, much further away than the time by which we’ll likely have the capacity to terraform neighboring worlds.
So, meanwhile, I do question whether we instead should look to settlements in discrete habitats that otherwise preserve natural environments that have been there for billions of years.
Perhaps with some O’Neill Cylinders thrown in there out in space.
Definitely an intriguing discussion of the terraforming possibilities in our Solar System. As I say, always an intellectually engaging topic.
Congratulations Adam! Now…
Terraforming our Sol system? Mere child’s play! Let us try hiding our entire planetary system from the rest of the galaxy….
http://nextbigfuture.com/2016/07/in-search-of-vanishing-stars-and.html
The paper online:
http://arxiv.org/abs/1606.08992
Nice to see the professional astronomy community thinking outside the box at last when it comes to ETI. Such expanded views cannot help but improve our chances for new scientific discoveries across the spectrum. It is the 21st Century, after all.
From my heavy biased opinion, Dyson Sphere or something equivalent is not the optimal solution in term of far future survival. I still don’t know how much we could achieve in quantum computation, but let’s assume that we could build some 100 qubits (2^100 ~ 10^30) quantum computers in about 300-500 years from now, by applying the method of clustering we could solve many difficult problems in which the current human brains aren’t powerful enough to solve. Hence I support building research stations or domes around the moon and some other “illegal” scientific activities in the outer regions ( > 50 AU ) in near future. Any project which takes longer than 1000 years to complete must be delayed since we might not have the same goal or change that goal in the future. Even Newton himself failed to realize the existence of Non-Euclidean geometry, if he had known the modern world would have had been a lot different.
This is all very interesting.
I think when it comes to space colonization, our species will be pulled in two different directions – the homeworld bias, and the human bias. The ‘homeworld’ bias refers to the desire to live on a planetary surface that is similar to Earth. The ‘human bias’ refers to the desire to maintain the human form and not modify ourselves biologically. These drives are in tension because adapting to another planet, even one that is terraformed, would involve adaptations and changes to our biology. For any planet that doesn’t have 1g of surface gravity, this would certainly happen. As it is, we simply don’t know enough about long-term exposure to 1/3 gravity to predict what effect it would have, but it’s safe to say that this would have significant long-term effects on colonists. Of course, by living in space habitats with a conditioned environment and artificial gravity provided by centrifugal force, we could maintain our biology while living in space. I don’t know how the human vs. homeworld conflict will play out in space colonization, but I think we will be pulled both ways.
Venus has almost earthlike gravity, which makes it an interesting target. I’ve decided to split my reply into two different posts to properly cover Venus.
onto Venus:
Venus has almost earthlike gravity, which makes it an intriguing target for terraforming. Could we turn Venus into a tropical second earth? I think it’s possible. One of the wilder ideas that occurred to me is to bombard Venus with hydrogen. Since its atmosphere is 96% carbon dioxide, all you would need is lots of hydrogen and a catalyst to trigger either the Bosch reaction or the Sabatier reaction – with Bosch creating water and graphite, and Sabatier creating water and methane. You could combine this with other ideas like solar shading to terraform. But then there’s the problem of Venus lacking a magnetosphere, which is a significant issue. Possibly you could restart core convection and the magnetosphere by speeding up the rotation of the planet, which would also provide a day/night cycle closer to what we’re used to. Maybe speeding up rotation could coincide with hydrogen bombardment.
This is all wild speculation, but I wanted to put it out there. A much more conservative solution would be floating colonies in the unmodified Venusian atmosphere.
What those who want a space habitat over a planet are going to discover, which xcalibur points out above, is people prefer worlds (planets and moons) over habitats. In order for a habitat to attract a good deal of support it would have to be bigger than the biggest bishop ring imaginable and this may simply not be possible. This is to say that a space habitat would have to take on the characteristics of a pseudo-world to appeal to most of humanity’s homeworld impulse. (On this matter, I find it attractive to know that mining would/could occur on a terraformed/caeliformed world while the idea of a space habitat depending on natural resources from the outside strikes me as undesirable.)
However, the gravity issue is incredibly important. Humanity really needs to seriously investigate whether different g poses any problems or not. The fellow who wrote To Crush The Moon, honestly believes that such a thing is possible to increase Lunar gravity if humanity possessed enough technology. Maybe the Moon and Mars would not be habitable at 0.1667/0.375 g but would become basically small low gravity neo-Earths at say 0.7 g. Perhaps such a radical approach will eventually be needed to terraform the moon (Mars?).
As for sending biological material instead of humans to the Ort Cloud and beyond, it just isn’t attractive to many people’s instincts. Why would any care if other systems (and the ort cloud) were colonized if they couldn’t get something out of it? People want the joy of genuine exploration and settlement, the reward of new lands to tame, shape, and flourish over, or at least the opportunities opened up on Earth/the familar Solar System as others depart for virgin territory elsewhere and reduce competition in humanity’s established stomping grounds. It woud be difficult no doubt to get people to the cloud and to other star systems but I think most of humanity will find it a more attractive project than having machines simply clone humans outside of established domains. (Though I bet colonists would love to have AI produce plants and animals and even perhaps more people when they arrive on terraformed planets in other systems.
I disagree. People have traditionally lived within small areas. Even today, people live out their lives in a single city. For those of us who travel, much of that is in a cylinder remote from contact with the ground. So each habitat with many square miles of living area will be quite adequate for most people, and travel will still be in cylinders between places.
Just as most people prefer staying in A/C hotels in the tropics, I see no reason why most people will be happier in environments that are “civilized” abodes rather than dealing with the inconveniences of permanently different gravities and atmospheres of partially terraformed planets, in addition to the high cost of escaping gravity wells when wishing to go somewhere different.
I think many people will live in cylinder/torus space habitats. However, I also believe there is an overarching drive to live on a habitable planet. It may not be entirely rational, but it’s an important factor, and it will drive colonization of planets and terraforming.
There’s also the issue of seeding earth life and creating ecosystems, which is best suited to a planet (notwithstanding the presence of native alien life and the accompanying moral dilemma).
I gave you my reason why people would be fine living in habitats. Perhaps you could offer something more than “belief”?
Perhaps you have something broader in mind when you say there is a drive to live on a habitable planet. Is there some physical or psychological aspect you are thinking of? Is there something that is important that cannot be replicated or simulated in some way? in extremis could one detect that one wasn’t living in a holodeck simulating a planet? Those pastoral O’Neill colony drawings were to show environments simulating those on Earth, however imperfectly. I suspect that economics will dictate that they look more like cities with defined parks, rather than wilderness with settlements. They may even degrade to slums. But I suspect that people living in them will call them home and prefer them to being back on a planet. If the dream of cheap travel between habitats becomes true, then habitat living with its far wider number of possible locations to travel to, may well be preferable to Earth. Earth might become that place with restored environments outside of controlled cities to visit physically or virtually.
Those reasons are valid. However, I do think there is a psychological aspect that leads to homeworld bias. The fact that most discussions of space colonization are centered on exoplanets and terraforming, rather than viable space habitats, is evidence of this.
There are also other issues with space habitats. Their limited scope would lead to dense urban living, and on-board natural ecosystems would be limited (an ecosystem needs lots of space to achieve maximum variety and vitality). There is also the specter of system malfunctions or even catastrophic accidents. If you live on a habitable planet, there is a sense of security against apocalyptic events. The danger is there, but the vastness and stability of a planet and its ecosphere is a buffer against all but the heaviest cosmic impacts. For a space habitat, the danger of annihilation is much more apparent. An asteroid hit, life support breakdown, or political turmoil leading to hydraulic despotism or destruction, are all serious risks.
That’s not to say that I’m against space habitats, I still think they’re an excellent solution. However, those issues and limitations are there. Individuals who prefer planetside living will have motives ranging from rural/pastoral living, avoidance of systemic danger, to a sky seen overhead.
In addition, you assume a high cost to escaping gravity wells. In a solar-system-wide civilization, we would use launch loops/startrams or a similar mechanism for cheap and efficient spaceports (while upfront investment is high, they would be far cheaper for routine launches).
I agree that more of us may end up living off-world than on Earth, and that this has significant implications for the Earth. But that’s another discussion.
As I’ve said before, I believe our race will be split between colonizing planets and living in space habitats (cylinder, torus, etc.) It will be both, not either/or.
If we have the technology to build habitable worlds we won’t need to colonize places that have inhabitants. And shouldn’t.
That appears to be a matter for the remote future to deal with. We’ll have our hands full getting a grip on our solar system for a while.
Late to the party, Terraforning.
Strangely enough with clever engineering, Venus is feasible.
Although Venus will be more expensive to terraform in both Energy & Material cost, than mars. It may be more suitable for colonization once
terraformed.
To get a shirtsleeve enviroment for Venus requires.
1)
Put a shade an lower the temps and freeze out the atmosphere as
was stated by Article.
2) H20 / N2 supply
During your wait for the planet to cool off, you can maneuver larger icy moonlets of 2-3 km in size and start bombarding Venus. (this could be done
it the latter years of terraforming so it doesn’t interfere with the cooling attempt. The nitrogen. Well, you can mine it from Triton, but why do
that?, you have to lift it into orbit and Neptune is pretty damned far. How about a ram scoop passing inside the Titan atmosphere. fleet of automated ships that are all engines plus a pressure vessel to accommodate hundreds Billions liters per ship. As long as you time things right you should be able
to have your scooper dive in and out then accelerate out of the Saturn
gravity well.
Once close in to Venus, Dump and run, let venus capture the Nitrogen, and return to rendezvous w/ Titan, using copius solar energy for power systems and propulsion.
3)
Day Night / Protection from Cosmic Radiation.
I don’t think it’s possible to give a 24 hr spin to Venus, that is close to
equivalent to moving the planet itself if it’s a hurried attempt. A non-starter.
You can create an orbital ring to cover about 60% of the equator and most of the mid lattitudes to create a pseudo day night cycle for the side facing the sun. For the dark side, you shades would have to have the ability to charge up with solar power and then light up the dark side.
These panels should be layered with gases at low PSI, that help to diminish Cosmic rays and solar particles/hard radiation.
Hopefully Mars will be viable colony in the near future,
but I would not bet on it, it only looks appealing because it is just
short of being habitable, (unfortunately it is just Short, of REALLY important things, that are not easily remedied)
Mars’ almost “habitable” features are mirages.
I agree that this makes a lot more sense than trying to spin up a planet. [ It is even easier to create even more perfect conditions with a space habitat. ;) ]
We could live inside Mars or the Moon or low gravity worlds via deep shafts in which rotating habitates are made and rotated, cap the top with a dome. Habitates can be many kilometers in diameter and simulate higher gravities than Earth with the forces taken up by the shaft walls.
We could, but why go through all that bother and extra complicated engineering, only to add an inconvenient gravity well? The logic of O’Neill’s suggestion hasn’t changed as far as I can see. Asimov called it planetary chauvinism. can you imagine the issues in trying to build an Island 3 sized habitat underground?
I do see building cities underground, and living with the lower g if possible, mitigating it with higher-g gyms and drugs, or populated with humans 2.0.
I too believe rotating habitats in space are better, but for the land lovers they can live in cities with rotating to torus’s to simulate gravity. Whole km diameter torus ‘s can be built in these shafts with access to the lower g planet when they leave them for exploration and play.
If we cleared out Jupiter’s radiation belts and then used it’s powerful magnetic field which would require a lot of energy we could then use the field of Jupiter to power interstellar craft. The power of the field is potentially in the hundreds of terrawatts or much more. If we calmed Io down by preventing ions taking off its surface it would be a lot safer. Now a means of extracting energy from the field maybe could be achieved by having a conductor connected from the surface of Io and allowed to dangle towards Jupiter where the fast moving field would generate power, this could to done on all the moons and on the little ones to moving them about.
If we were to terraform Venus, I wonder whether the inherently needed solar shade could double as an in-space solar power generator. The shade then would both intercept the “excess” solar irradiance while converting some of it to usable energy to be beamed to the planet for use in terraforming operations and later human settlements.
Would imagine also that such a shade could tend to act as a huge solar sail, even while parked at a gravitationally neutral Lagrangian point. Having the shade double as a solar power generator also could power drives to keep the shade on station.
Using hydrogen from deeper in the solar system does provide the two-fer solution of reducing carbon dioxide while also producing water, as discussed in this paper by Paul Birch:
http://buildengineer.com/www.paulbirch.net/TerraformingVenusQuickly.pdf
Birch also conceptualized a method to spin the planet’s rotation up to a 24-hour day within 30 years.
http://buildengineer.com/www.paulbirch.net/SpinAPlanet.pdf
An approximately 80% water world with roughly one g and a 24 hour day. The clear starlit nights free of Earth-based light pollution no doubt would be awesome.
Might be able to overcome my aesthetic reservations for that.
Guess a planet with a surface that can’t be seen from Earth in visible light and with a surface temperature in excess of 800 degrees Farenheit gets less aesthetic respect in the overall scheme of things, lol.
That is a really interesting paper.
As I mentioned in my other post, a magnetosphere is important for a habitable planet, and Venus’ lack thereof is a significant obstacle. One possibility is using the sun-shade concept to shield the planet from radiation. But there may be a better, more permanent solution. My hypothesis is that the rotation rate of a planet and its magnetosphere are directly correlated – a higher rotation rate leads to a stronger internal dynamo and thus a stronger magnetosphere. Therefore, I believe that if Venus’ rotation was sped up, this would ‘power on’ a magnetosphere. Having an earthlike day/night cycle is convenient, but the magnetosphere is the primary consideration.
With the Birch rotation concept, along with the Bosch/Sabatier chemical reactions, it seems that terraforming Venus is an attainable long-term goal.
Had been thinking about the magnetosphere a bit after penning the above, while looking over the other notes including yours.
As backdrop, the Wikipedia section on Venus’ magnetic field and core suggests that: (a) the lack of a functioning dynamo currently could be due to a lack of convection in the planet’s core; (b) the lack of convection could be due to a global resurfacing event that led to reduced heat flux through the crust, trapping heat inside with little internal differentiation; and (c) the internal heat is just reheating the crust. Little is known about Venus’ internal structure, with the possibilities ranging from the core already being completely solidified, to the liquid portion all being the same temperature, to there being no solid inner core – with all of the possibilities hinging upon the concentration of sulfur, which is unknown. However the internal structure of Venus is configured, though, it’s clearly not conducive to creating a strong magnetosphere currently.
The Wikipedia article further suggests that “[t]he principal difference between the two planets [Earth and Venus] is the lack of evidence for plate tectonics on Venus, possibly because its crust is too strong to subduct without water to make it less viscous.”
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Venus (text at notes 54-55 & 84-90)
That last bit got me thinking.
The addition of hydrogen to make water on Venus thus could have the added ultimate benefit of re-kickstarting plate tectonics, cooling the crust, and further facilitating differentiation of temperature inside the planet. That perhaps then could lead to internal convection, leading to a more fully functioning dynamo, and thereby contributing to a stronger Venerean magnetosphere.
In short, if I’m understanding the science correctly, the introduction of large quantities of water on Venus could work hand-in-glove with the spinning up of the rotation speed to help produce a stronger magnetosphere. All through induced-but-ultimately-natural processes rather than the creation of an artificial magnetosphere.
The trick would be to use the water to cool and then increase the viscosity of the crust without producing a permanent steam bath that just perpetuated the greenhouse effect. Might take a few steam-atmospheric cooling-precipitation cycles to bleed off the residual heat from the crust all while hopefully avoiding getting stuck again in greenhouse mode. Limiting the solar irradiance that reaches Venus thus perhaps is only part of the cooling challenge — taking into account as well the residual heat in the crust coming from internal heating.
And I would think that restarting plate tectonics on Venus would not be a very seismically “quiet” event. There likely would be a considerable at least adjustment period with large planetquakes as well as tsunamis on any oceans that have formed. That tumult, however, might produce more differentiation in Venus’ currently relatively undifferentiated terrain – producing more land masses jutting up amidst those seas.
All of which depends as well on what exactly is going on inside Venus with the state of its core, which remains a large unknown.
As a sailor, I would love to sail the seas of Venus under that clear, starlit night.
Might take a while, however, to produce that stable balance that our Earth achieves seemingly so effortlessly, despite our best efforts sometimes to muck it all up.
I’m still confused as to how much energy it actually takes to get to the nearest star. I keep running into a paradox between the kinetic energy required by the work energy theorem in the earths reference frame and the actual energy expended from the ships point of view. In this though experiment, ignore mass of the exhaust and consider that the engine works by some method such as Shawyer’s EM drive for convenience.
Take as given that a ship gains a velocity v for an energy E with respect to any inertial reference frame it’s in. Observers on the ship and earth agree that it takes E to start from rest wrt earth and get to v. An observer on the ship would then say it takes E to go from its new rest frame to a speed v wrt that frame. But reference frame velocities add linearly non-relativistically. So the ship is going 2v wrt to earth. Yet the ship expended only 2E to be going at 2V wrt earth, rather than 4E as the earth observer would calculate its kinetic energy. This suggests that the energy requirement from the ships point of view to gain a velocity wrt earth grows only linearly with velocity wrt earth, not quadratically. I only need enough energy to boost my speed wrt the initial frame I am in at the moment. This implies that the work energy theorem cannot naively be applied from the the earths fixed reference frame for a constant thrust rocket or it implies, I’m very confused.
The laser sail example from above that gets to half light speed in 190 days stoked my thought. In that case the power comes from outside the rocket though and maybe what important is the constant thrust, not the kinetic energy as calculated from the earths reference frame. Kinetic energy is not an invariant. If the energy source is carried with the ship as in the EM drive, my previous critique of Shawyer’s intersteller probe may have been naively wrong.
If anyone has the time or interest I would appreciate a response to this quandary.
An even simpler example. Consider firing a bullet from a gun with velocity v. Call its kinetic energy K. Now, consider a big plane flying at the same v. Fire the gun in the direction of motion inside the plane. The kinetic energy wrt the planes frame is K. But the bullet is going at 2v wrt the ground if velocities add linearly as they do so the kinetic energy as computed from the ground is 4K. It started with K wrt the ground, being on board the plane moving at v yet the chemical energy released was the same in both cases. So the question is how did the bullet end up with 4K of kinetic energy wrt the ground frame when only K of additional chemical energy was added to its initial energy of K wrt the ground? I’m stumped. Thanks.
Robert, you might want to consult an introductory physics textbook. That is not meant as an insult. These are some basic concepts involved here.
First, let’s ignore the *how* and look at the results of firing the gun. Consider momentum, not energy: p=mv. Elastic interactions between the bullet and the target preserve the total momentum. Further, the interactions scale linearly with mass and velocity, as you may have already suspected. Typical problem statements in the textbooks use billiard balls on a frictionless table. Of course there are vectors involved since velocity is a vector, although you can keep it simple and only consider axial collisions.
Second, guns (or other mechanisms) don’t simply add energy to the bullet. This is where the *how* matters. Let’s assume the gun is firmly affixed to the plane (although this really should be done in space so that gravity and air resistance can be disregarded). The explosive charge pushes on both the bullet and the gun. Since the bullet is free to move forward and the barrel is resilient there is an equal and opposite reaction on the momentum and kinetic energy of the plane in accord with Newton’s laws. The energy of the explosion generates heat and kinetic energy which accelerates the bullet forward and the plane backward. Conservation of energy should make it clear what happens, and you can work through the detailed calculations as an exercise.
Third, when velocity is high and relativistic, conservation laws still apply, however the calculations are more complex. Only take this step once you understand the Newtonian dynamics quantitatively.
First, thanks. I wrote a long and detailed reply but that seems to have gotten lost after I hit the button. Oh well…
I’ve done the math and am aware of everything you said. In that example the bullet borrows some of the planes energy to gain additional kinetic energy. The problem is that the books don’t go deep enough into my quandary.
First, I assume certain fundamentals. Acceleration is absolute and velocity is relative thus a ship, in any inertial frame, can change its velocity which will be seen by all observers in all other inertial frames as the same change and an engine burn can be measured in any frame as a fixed release of say chemical energy like the bullet when observed from a any reference frame. Do we agree?
I’ll simplify my question. Assume I have a ship in which the engine can deliver a one second burst and gain 10m/s velocity wrt a beacon I set out when I was not accelerating. The beacon establishes a frame. I left the earth a while ago and I plan to reach a terminal velocity of c/2 wrt earth frame then coast. Say I am just 10m/s short of my goal. I set a beacon and burn the engine to get that last 10 m/s velocity wrt to the earth and the beacon.
How much energy did I need? The observer on earth says I needed about 1.5 billion joules per kg to increase my speed by that last 10m/s. That’s c/2 squared minus (c/2-10) squared divided by 2 per kg mass. But relative to my space beacon, I accelerated from zero to 10m/s using 50 Joules per kg to gain 10m/s. One can book keep the energy from any frame as long as one is consistent. But only one frame can tell me the cost at say one dollar per Joule to run my engine. That’s the number I want.
Note that I am not questioning fundamental physics at all, just trying to discern the real cost of running the engine. Thanks.
You are attempting a Newtonian calculation of the velocities and dynamics yet you are in a regime where you need to do a Lorentz transformation (boost). Velocities do not add linearly!
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Lorentz_transformation#boost
The energy is as calculated in the ship’s comoving frame. To an outside (not comoving) observer the duration of engine burn and the velocity delta are different. Either way total energy and momentum are equal and conserved, *if* you do the required Lorentz transformation between frames.
If you add ‘a’ joules to the ship’s kinetic energy of X and you then crash into something the interaction will see X+a joules of kinetic energy. Both the crasher and the crashee will agree.
I recommend you buy a textbook on spacetime physics if you want to learn this stuff.
Thanks. I have Wheeler’s Spacetime Physics but in my example I can add the velocities because the Lorentz boost is insignificant since one of the velocities is always small.
I agree with your point of view, the energy costs are calculated in the ships co moving frame. Then physicist Bob Park, who famously derides the concept of interstellar travel by claiming that the energy costs are the final kinetic energy in the earths frame, which is astronomical, is simply wrong. This is also implied in the appendix of the Starflight Handbook by Mallove and Matloff. Thanks again.
As I understand project Deadalus for example, a constant stream of 250 pellets per second produces a constant thrust and an acceleration which even increases as the propellant mass is used up. All observers should agree that the ships energy supply is used up linearly yet the ships kinetic energy wrt earth grows quadratically.
“the energy costs are calculated in the ships co moving frame”
To be clear, it can be calculated in any frame. It’s simplest in the comoving frame since you don’t have to muck about with Lorentz transforms.
I get the feeling that it will turn out that the most efficient and tractable
way to send humans to solar systems beyond a few light years will
be individually in rather lightweight small ships. These smaller ships
would be sent at first with high automation and equipment for self assembling a braking approaching and accelerating outgoing craft type infrastructure. These first pioneering missions would be expensive as they will require many extra units to help brake and guide the components into proper position.
Once the infrastructure is set up, we are talking about ships weighing something like 5ooKG. With highly capable nanomachines that would allow intensive recyclying and living of the local resources . The need for the light weight is obvious it needs to take advantage of time dilation. How much. 80 LY compressed to 1/4 of a year. (The unmanned versions would be much heavier and thus not have nearly this high a time dilation.)
dilation 1:240. Relativistic mass is what restrains (as always) this approach
a ship and crew weighing 500KG will mean the last stage of acceleration
to .9999c will be the equivalent of pushing a payload of 120 Metric tons. If this seems Very difficult. Then try 18,545 relativistic metric tons for ship the size of Sky Lab, I think one is tractable in the near future, the other in the distant future.